Topical Fluoride Application
What is Fluoride?
Fluoride is a mineral that is found in all natural water sources. It is the ionic form of the trace element Fluorine, which is commonly found in the environment. Fluorine reaches water sources by leaching from soil and rocks into groundwater.
What is Fluoride Varnish and its role in decay prevention?
Fluoride as a mineral, when used as directed or within the context of Professionally Applied Topical Fluoridation programs, is a safe and effective agent that can be used to prevent and control dental caries. Topical fluorides strengthen teeth already present in the mouth, making them more decay resistant and become incorporated into forming tooth structures.
Mechanism of Action of Fluoride?
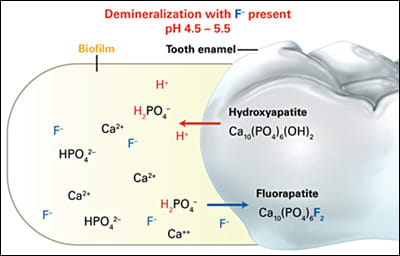
- On external application of Fluoride, the interaction of Fluoride with the mineral component (Hydroxyapatite) of teeth produces a fluorohydroxyapatite (FHAP or FAP) mineral by substitution of OH– with F–. This results in increased hydrogen bonding, a more dense crystal lattice, and an overall decrease in solubility. The incorporation of Fluoride into the hydroxyapatite (HAP) lattice may occur while the tooth is forming or by ion exchange after it has erupted.
- In addition to protecting against demineralization, another way in which Fluoride interacts with enamel to reduce dissolution is through remineralisation. This is a process in which partially dissolved enamel crystals can accept minerals for mineral deposition . Therefore, remineralization helps counteract demineralization and an equilibrium then develops between the two processes. The carious lesion occurs when the demineralization process outweighs the remineralization process and net damage occurs. So, Fluoride helps increase remineralisation and decrease demineralisation.
- The third way Fluoride prevents caries occurrence is by changing the outermost structure of enamel from Hydroxyapatite to Fluorohydroxyapatite and Fluoroapatite. Formation of fluorohydroxyapatite (FHAP or FAP) results in a mineral with an even greater level of acid resistance. A greater level of acid resistance leads to greater resistance to caries.
When can Fluoride application be started?
Fluoride application can be carried out for children ages 6 months to 16 years who are at high risk for tooth decay and whose primary drinking water has a low Fluoride concentration. The frequency of application increases in children with greater risk of dental caries.
What are the various forms of fluoride?
Fluoride can be either self-applied at home or it could be professionally applied in a dentist’s clinic. Self-applied fluoride is in the form of toothpastes and mouthwashes containing Fluoride. These agents have much lesser quantity of Fluoride and thus have to be used for longer duration with limited caries protective capacity. Professionally applied fluoride agents are in the form of Solutions, Gels, Varnishes and SDF all of which have very high quantity of Fluoride, which makes the preparation caries protective.


What should I know about fluoride varnish?
Fluoride varnishes are available as sodium fluoride (2.26% [22,600 ppm] Fluoride) or difluorsilane (0.1% [1,000 ppm] Fluoride) preparations. A typical application requires 0.2 to 0.5 mL, resulting in a total Fluoride ion application of approximately 5 to 11 mg. High-concentration fluoride varnish is painted by dental surgeon directly onto the teeth and sets when it comes into contact with saliva. Fluoride varnish is not intended to adhere permanently; this method holds a high concentration of fluoride in a small amount of material in close contact with the teeth for several hours. Varnishes must be reapplied at regular intervals with at least 2 applications per year needed for sustained benefit.
Method of Application
Steps of application of Fluoride varnish are as follows:
- Isolation and drying the teeth with gauze. We may isolate a quadrant of teeth at a time.
- Application of a thin layer of the varnish to all surfaces of the teeth.
- The varnish sets quickly. You need not worry about moisture (saliva) contamination
What should I know about SDF?
Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF) is a colorless liquid that contains 5.0% to 5.9% Fluoride (48000 ppm). Similar to Fluoride varnish, SDF must be applied professionally. There is overwhelming research to support the use of SDF in Caries Control and management and in treating Dental Sensitivity.
SDF has been shown to lower caries risk of the adjacent tooth surface. SDF has also shown efficacy in management of root caries in children as well as the elderly.
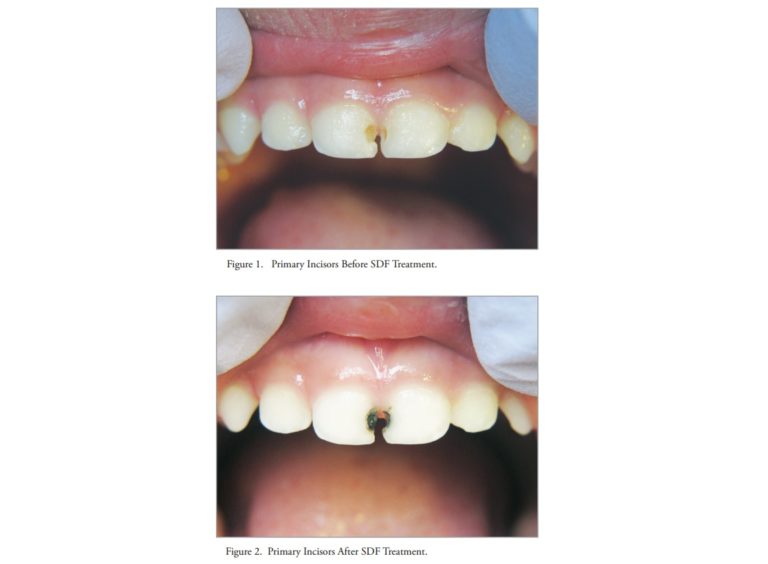
- It also has additional applicability as an interim approach for managing problematic caries in individuals currently unable to tolerate more involved dental treatment such as very young children who lack co-operative ability.
- Semi-annual application (every 6 months) of SDF has been reported to have sustained benefit.
- Its potential downsides include a reportedly unpleasant metallic taste, potential to irritate gingival and mucosal surfaces, and the characteristic black staining of the tooth surfaces to which it is applied.
